
A 220 ohm resistor has red, red, brown, and gold bands. Each band stands for a number or a multiplier. Reading these bands tells you the resistor’s value. Knowing the right value helps circuits work better and safer. Studies show that using the right resistor lowers failure rates.
Key Takeaways
-
A 220 ohm resistor helps control electric current. It protects parts like LEDs and keeps circuits safe.
-
You can spot a 220 ohm resistor by its color bands. The bands are red, red, brown, and gold for 4-band types.
-
Picking the right resistor with good tolerance and power rating helps circuits work better and stay safe.
220 Ohm Resistor
Definition
A 220 ohm resistor is a small part used in circuits. It controls how much electric current can pass through. The value of 220 ohms means it slows the current by 220 ohms. This number is important because it helps set safe current levels. You can spot this resistor by its red, red, brown, and gold bands. Many people use it in projects because it lets enough current flow but keeps parts safe. The resistor can look different, but its job is always to control current.
Circuit Role
The 220 ohm resistor is used in many types of circuits. It is chosen often because it works for many jobs. Here are some ways people use a 220 ohm resistor:
-
In LED circuits, it keeps the LED from getting too hot.
-
It helps make voltage divider circuits to lower voltage for other parts.
-
The resistor sets the right bias for transistors so they work well.
-
It can help feedback circuits in power supplies keep voltage or current steady.
People like the 220 ohm resistor for current limiting and voltage division. It gives enough resistance to protect parts but does not stop too much current. This makes it a good choice for many electronics projects.
Resistor Color Code
Color Code System
The resistor color code helps people quickly find the value of a resistor. Each color stands for a number, a multiplier, or a tolerance. The most common system uses colored bands painted on the resistor body. The first bands show the main numbers, the next band shows the multiplier, and the last band shows how much the value can change (tolerance).
Here is a table that shows what each color means in the resistor color code system:
| Color | Digit Value | Multiplier (Power of 10) | Tolerance (%) | Temperature Coefficient (ppm/°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 10^0 (1) | N/A | N/A |
| Brown | 1 | 10^1 | ±1 | 100 |
| Red | 2 | 10^2 | ±2 | 50 |
| Orange | 3 | 10^3 | N/A | 15 |
| Yellow | 4 | 10^4 | N/A | 25 |
| Green | 5 | 10^5 | ±0.5 | N/A |
| Blue | 6 | 10^6 | ±0.25 | 10 |
| Violet | 7 | 10^7 | ±0.1 | 5 |
| Gray | 8 | 10^8 | ±0.05 | N/A |
| White | 9 | 10^9 | N/A | N/A |
| Gold | N/A | 10^-1 | ±5 | N/A |
| Silver | N/A | 10^-2 | ±10 | N/A |
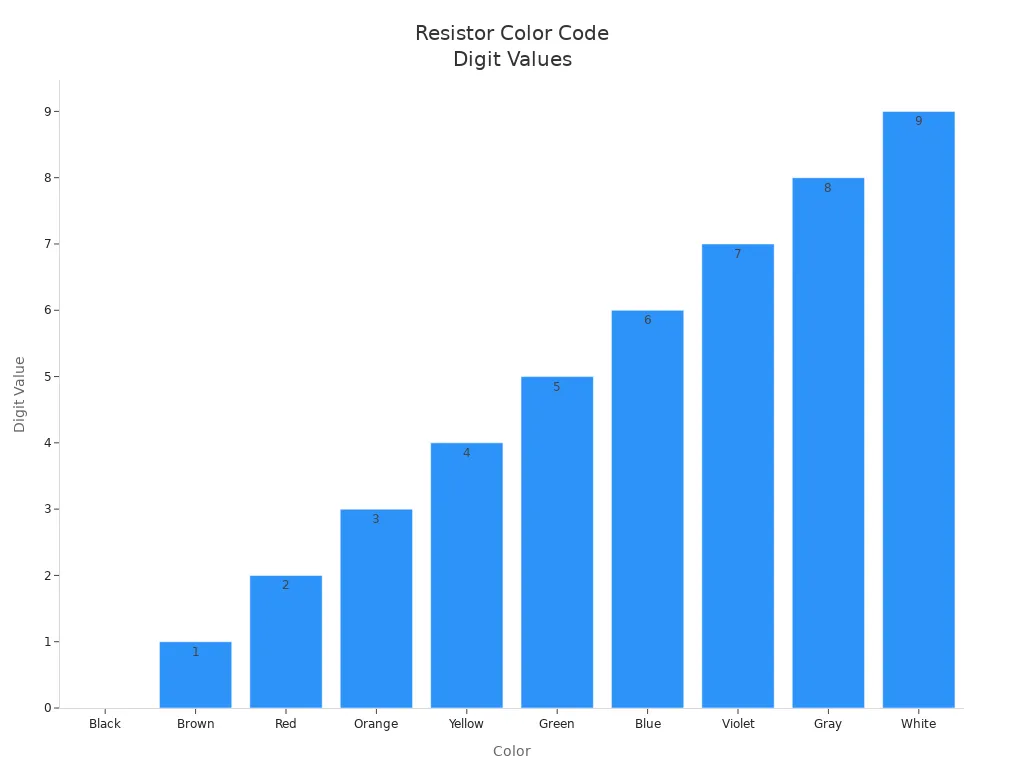
The color code system follows international standards. These standards make sure that anyone, anywhere, can read a resistor and know its value.
Identifying 220 Ohm Resistor
A 220 ohm resistor uses the color code to show its value. People can find this resistor in both 4-band and 5-band types. Here is how to read each one:
-
4-Band 220 Ohm Resistor
-
First band: Red (2)
-
Second band: Red (2)
-
Third band: Brown (multiplier ×10)
-
Fourth band: Gold (tolerance ±5%)
The value is 22 × 10 = 220 ohms.
-
-
5-Band 220 Ohm Resistor
-
First band: Red (2)
-
Second band: Red (2)
-
Third band: Black (0)
-
Fourth band: Brown (multiplier ×10)
-
Fifth band: Gold (tolerance ±5%)
The value is 220 × 1 = 220 ohms.
-
Tip: If the color bands look faded, try to use a magnifying glass. If the value is still unclear, use a multimeter to measure the resistance. This tool gives a digital reading and helps confirm the resistor value.
Some resistors use a 6-band code, which adds a temperature coefficient band. For a 220 ohm resistor, the bands would be red, red, black, black, brown, and a sixth band for temperature.
Color Code Table
The tables below show the standard color code for resistors, including the 220 ohm resistor for both 4-band and 5-band types.
| Resistor Type | Band 1 | Band 2 | Band 3 (Digit/Multiplier) | Band 4 (Tolerance) | Band 5 (Optional) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-Band | Red (2) | Red (2) | Brown (×10) | Gold (±5%) | N/A |
| 5-Band | Red (2) | Red (2) | Black (0) | Brown (×10) | Gold (±5%) |
| 6-Band | Red (2) | Red (2) | Black (0) | Black (×1) | Brown (±1%) + Temp Coefficient |
Note: The 220 ohm resistor is easy to spot once you know the color code. Always check the bands from left to right, starting with the band closest to the edge.
The resistor color code system helps people find the right resistor for their circuits. Using the correct 220 ohm resistor keeps electronic parts safe and working well.
Features and Applications
Key Features
A 220 ohm resistor has many helpful features for circuits. Most 220 ohm resistors have a standard tolerance. Tolerance means how much the real resistance can change from what is written. The table below shows common tolerance values and what they mean:
| Specification | Typical Values for 220 Ohm Resistors | Effect on Circuit Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | 5%, 1% | Tolerance tells how much the resistance can change from 220 ohms. If the tolerance is 5%, the resistance can be between 209 and 231 ohms. This can change how exact the circuit is. A lower tolerance, like 1%, means the resistor is more accurate. People use these in circuits that need to be very precise. A higher tolerance, like 5%, is fine for most regular uses. |
Most 220 ohm resistors can handle 0.25W or 0.5W of power. This number shows how much heat the resistor can safely handle. A 220 ohm resistor is small and shaped like a cylinder. It has colored bands to help people know its value fast. The temperature coefficient helps the resistor keep the same resistance, even if it gets hotter or colder.
Common Uses
The 220 ohm resistor is used in many ways in electronics. Engineers and people who build things use it for these reasons:
-
It keeps LEDs safe by stopping too much current.
-
It helps control current in small devices, saving energy.
-
It is used in voltage divider circuits to set voltages.
-
It helps transistors work right by setting their bias.
-
It helps circuits work well by keeping resistance steady.
-
Its power rating stops it from breaking or wasting energy in small circuits.
Tip: Picking the right 220 ohm resistor with the best tolerance and power rating makes your project safer and work better.
To find a 220 ohm resistor, look for the tolerance band first. Then, use a chart to figure out what each color band means. Beginners can learn the color codes and check what kind of resistor they have. They can also use a multimeter to make sure the value is right. Doing these steps helps keep every resistor in a project safe. The 220 ohm resistor is a favorite for learning and making circuits. Picking the right resistor makes circuits work better and safer. Every electronics project gets better when you check and pick each resistor carefully.
FAQ
What does a 220 ohm resistor do in a circuit?
A 220 ohm resistor limits the flow of current. It protects sensitive parts like LEDs and helps keep the circuit safe and stable.
How can someone test a resistor’s value?
A person can use a digital multimeter. Place the resistor between the probes. The display shows the resistance value in ohms.
Can a resistor burn out?
Yes, a resistor can burn out if it handles too much power. Always check the power rating before adding a resistor to any project.
Written by Jack Elliott from AIChipLink.
AIChipLink, one of the fastest-growing global independent electronic components distributors in the world, offers millions of products from thousands of manufacturers, and many of our in-stock parts is available to ship same day.
We mainly source and distribute integrated circuit (IC) products of brands such as Broadcom, Microchip, Texas Instruments, Infineon, NXP, Analog Devices, Qualcomm, Intel, etc., which are widely used in communication & network, telecom, industrial control, new energy and automotive electronics.
Empowered by AI, Linked to the Future. Get started on AIChipLink.com and submit your RFQ online today!













